
Digital Transformation
The current trends of automation and data exchange in manufacturing, also referred to as “Industry 4.0” or the “Industrial Internet of Things” (IIoT), are based upon digitization. By converting analog signals, sounds, images, texts, and other information into a computer-readable format, digitization has been transforming industries for decades. For manufacturers to make sense of all these bits of information, the data must be transported from numerous sensors and equipment on the factory floor and processed for humans or other machines to make informed decisions in real-time.
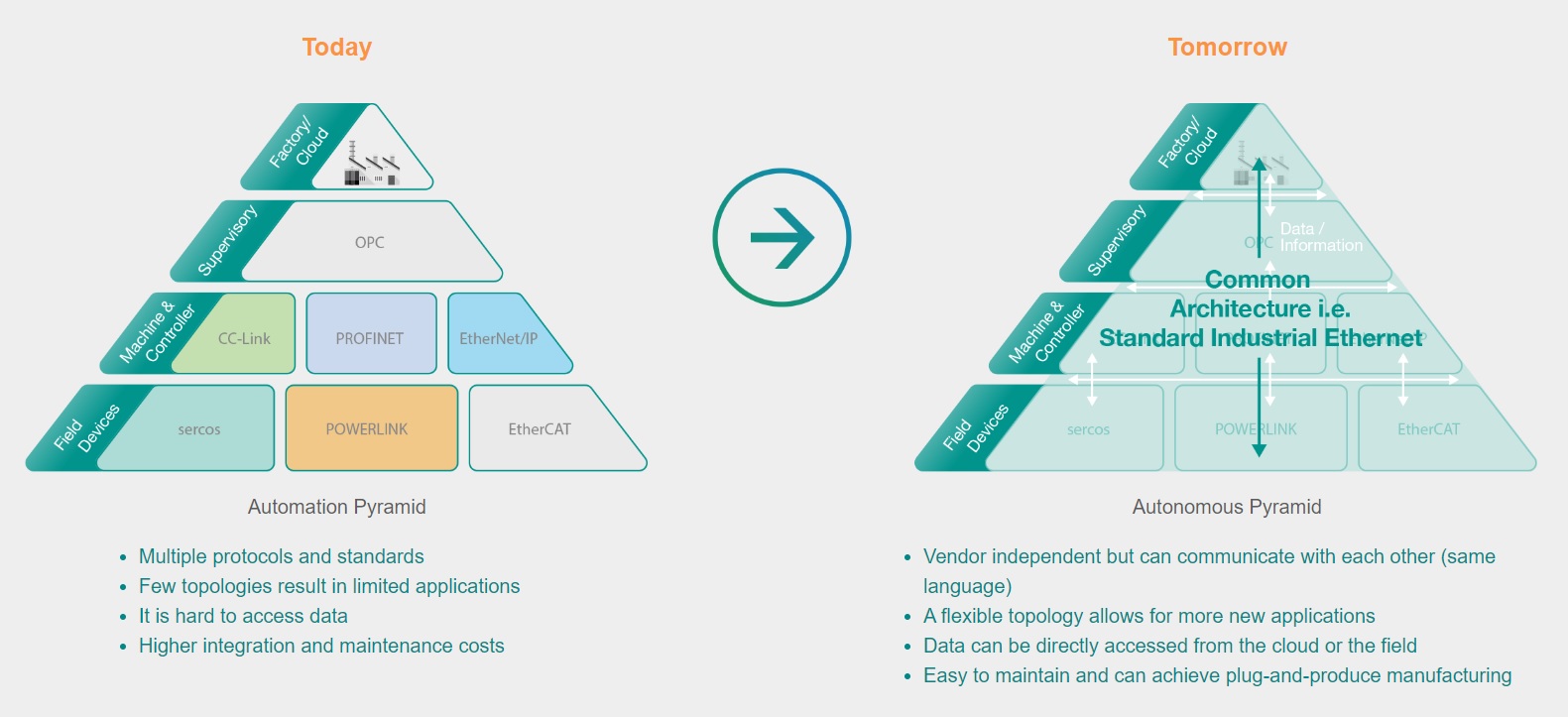
The Road Toward IIoT and Industry 4.0
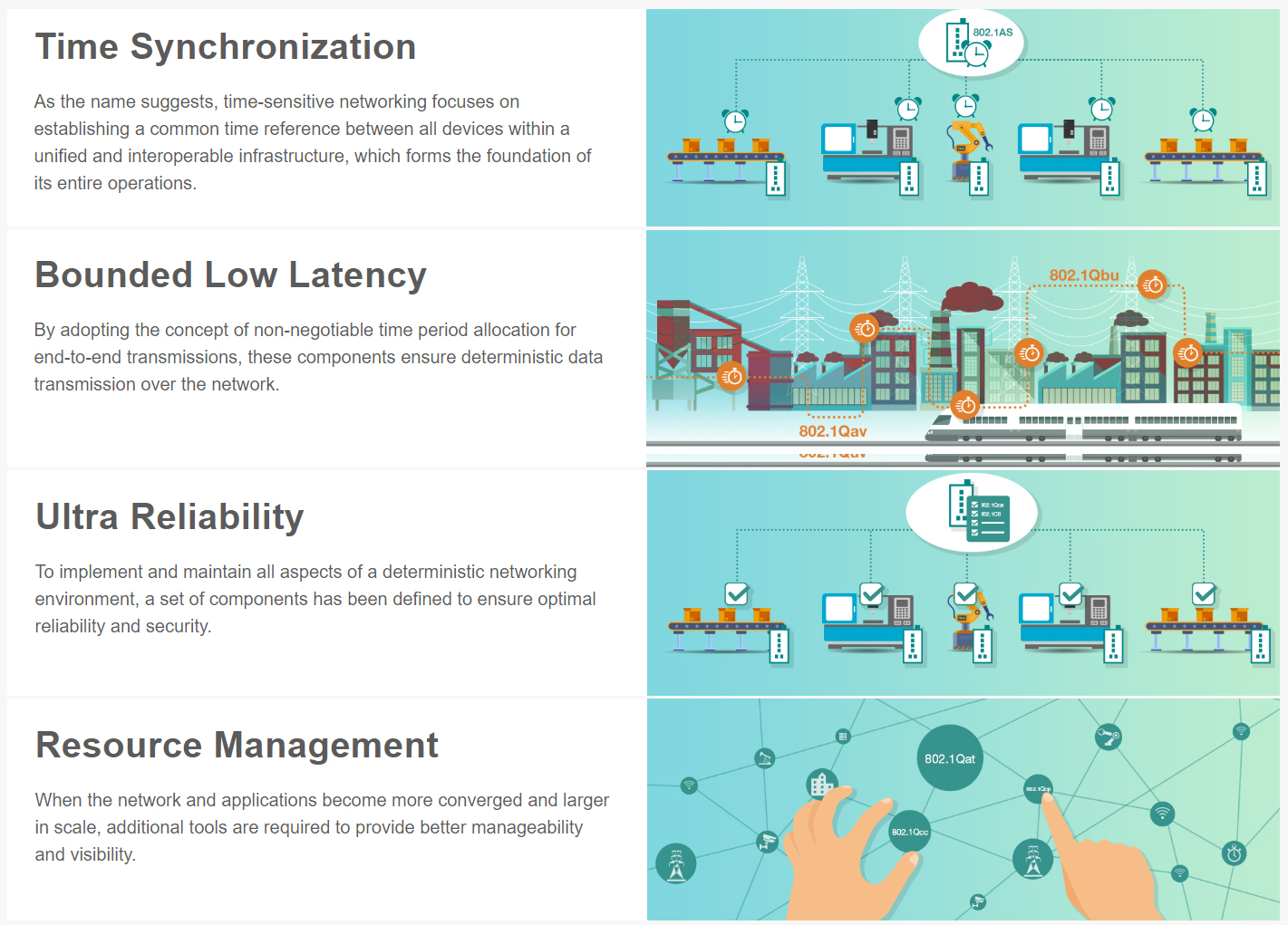
What Is TSN?
TSN is a collection of standards that enables deterministic messaging over standard Ethernet networks. As defined by the Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers (IEEE), TSN involves a form of network traffic management to ensure non-negotiable time frames for end-to-end transmission latencies. Consequently, all TSN devices must synchronize their clocks with each other and use a common time reference to support real-time communications for industrial control applications.
See 6 Real-world TSN Applications Powered by Moxa and Partners
Moxa was invited by CLPA and Mitsubishi Electric to Taipei Automation 2021 to demonstrate six real-world TSN applications powered by Moxa and thepartners. During the event, Moxa showcased applications with CLPA, Mitsubishi Electric, Intel, port GmbH, Orisol, and Sumyen Automation, which realized the concept of one unified network across different automation scenarios.
Simulating a Smart Factory Network With and Without TSN
Real-time communication is crucial for smart factory automation as networks grow in scale and complexity. Let's see how Time-sensitive networking (TSN) realizes deterministic communication in converged applications.




-150x150.png)


